SOC Fundamentals
Learn the fundamentals of a Security Operations Center (SOC), including the roles, responsibilities, and tools used by SOC analysts. Based on the TryHackMe SOC Fundamentals room.
Intro to SOC
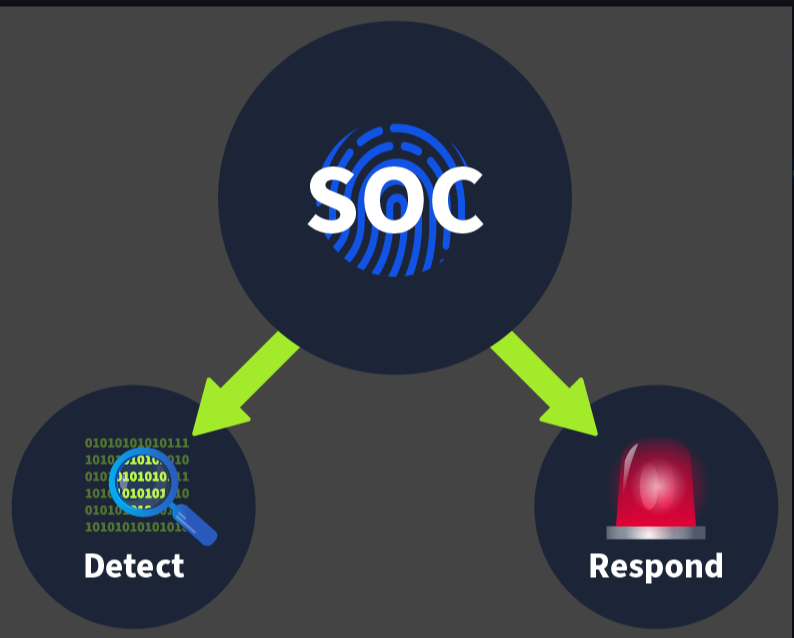
A SOC (Security Operations Center) is a dedicated facility operated by a specialized security team. This team aims to continuously monitor an organization’s network and resources and identify suspicious activity to prevent damage. This team works 24 hours a day, seven days a week.
The main focus of the SOC team is to keep Detection and Response intact. The SOC team has some resources available in the form of security solutions that help them achieve this. These solutions integrate the whole company’s network and all the systems to monitor them from one centralized location. Continuous monitoring is required to detect and respond to any security incident.
Detection
- Detect vulnerabilities: A vulnerability is a weakness that an attacker can exploit to carry out things beyond their permission level. A vulnerability might be discovered in any device’s software (operating system and programs), such as a server or computer. For instance, the SOC might discover a set of MS Windows computers that must be patched against a specific published vulnerability. Strictly speaking, vulnerabilities are not necessarily the SOC’s responsibility; however, unfixed vulnerabilities affect the security level of the entire company.
- Detect unauthorized activity: Consider the case where an attacker discovered the username and password of one of the employees and used them to log in to the company system. It is crucial to detect this kind of unauthorized activity quickly before it causes any damage. Many clues, such as geographic location, can help us detect this.
- Detect policy violations: A security policy is a set of rules and procedures created to help protect a company against security threats and ensure compliance. What is considered a violation would vary from company to company; examples include downloading pirated media files and sending confidential company files insecurely.
- Detect intrusions: Intrusions refer to unauthorized access to systems and networks. One scenario would be an attacker successfully exploiting our web application. Another would be a user visiting a malicious site and getting their computer infected.
Response
- Support with the incident response: Once an incident is detected, certain steps are taken to respond to it. This response includes minimizing its impact and performing the root cause analysis of the incident. The SOC team also helps the incident response team carry out these steps.
There are three pillars of a SOC. With all these pillars, a SOC team becomes mature and efficiently detects and responds to different incidents. These pillars are People, Process, and Technology.
The People are known as the SOC team. This team has the following roles and responsibilities:
SOC Analyst (Level 1):
Anything detected by the security solution would pass through these analysts first. These are the first responders to any detection. SOC Level 1 Analysts perform basic alert triage to determine if a specific detection is harmful. They also report these detections through proper channels.SOC Analyst (Level 2):
While Level 1 does the first-level analysis, some detections may require deeper investigation. Level 2 Analysts help them dive deeper into the investigations and correlate the data from multiple data sources to perform a proper analysis.SOC Analyst (Level 3):
Level 3 Analysts are experienced professionals who proactively look for any threat indicators and support in the incident response activities. The critical severity detection reported by Level 1 and Level 2 Analysts are often security incidents that need detailed responses, including containment, eradication, and recovery. This is where Level 3 analysts’ experience comes in handy.Security Engineer:
All analysts work on security solutions. These solutions need deployment and configuration. Security Engineers deploy and configure these security solutions to ensure their smooth operation.Detection Engineer:
Security rules are the logic built behind security solutions to detect harmful activities. Level 2 and 3 Analysts often create these rules, while the SOC team can sometimes also utilize the detection engineer role independently for this responsibility.SOC Manager:
The SOC Manager manages the processes the SOC team follows and provides support. The SOC Manager also remains in contact with the organization’s CISO (Chief Information Security Officer) to provide him with updates on the SOC team’s current security posture and efforts.
Note: The roles in the SOC team can increase or decrease depending on the size and criticality of the organizations.
Alert Triage
The alert triage is the basis of the SOC team. The first response to any alert is to perform the triage. The triage is focused on analyzing the specific alert. This determines the severity of the alert and helps us prioritize it. The alert triage is all about answering the 5 Ws. What are these 5 Ws?
Technology
Having the right People and Processes in place would never be enough without security solutions for detection and response. The Technology portion in the SOC pillars refers to the security solutions. These security solutions efficiently minimize the SOC team’s manual effort to detect and respond to threats.
An organization’s network consists of many devices and applications. As a security team, individually detecting and responding to threats in each device or application would require significant effort and resources. Security solutions centralize all the information of the devices or applications present in the network and automate the detection and response capabilities.
Let’s get a brief understanding of some of these security solutions:
SIEM (Security Information and Event Management):
SIEM is a popular tool used in almost every SOC environment. This tool collects logs from various network devices, referred to as log sources. Detection rules are configured in the SIEM solution, which contains logic to identify suspicious activity. The SIEM solution provides detections after correlating them with multiple log sources and alerts us in case of a match with any of the rules. Modern SIEM solutions surpass rule-based detection, offering user behavior analytics and threat intelligence capabilities. Machine learning algorithms further enhance these detection capabilities.Note: The SIEM solution only provides the detection capabilities in a SOC environment.
EDR (Endpoint Detection and Response):
EDR provides the SOC team with detailed real-time and historical visibility into endpoint activity. It operates at the endpoint level and can execute automated responses. EDR has extensive detection capabilities, allowing detailed investigations and response actions with just a few clicks.Firewall:
A firewall functions purely for network security and acts as a barrier between internal and external networks (such as the Internet). It monitors incoming and outgoing network traffic and filters unauthorized traffic. Firewalls also contain detection rules that help identify and block suspicious traffic before it reaches the internal network.Other Security Solutions:
Several other security solutions play unique roles in a SOC environment, such as:- Antivirus
- EPP (Endpoint Protection Platform)
- IDS/IPS (Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems)
- XDR (Extended Detection and Response)
- SOAR (Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response)
The decision on which technologies to deploy in a SOC is made after careful consideration of the organization’s threat surface and available resources.
Practical Challenge
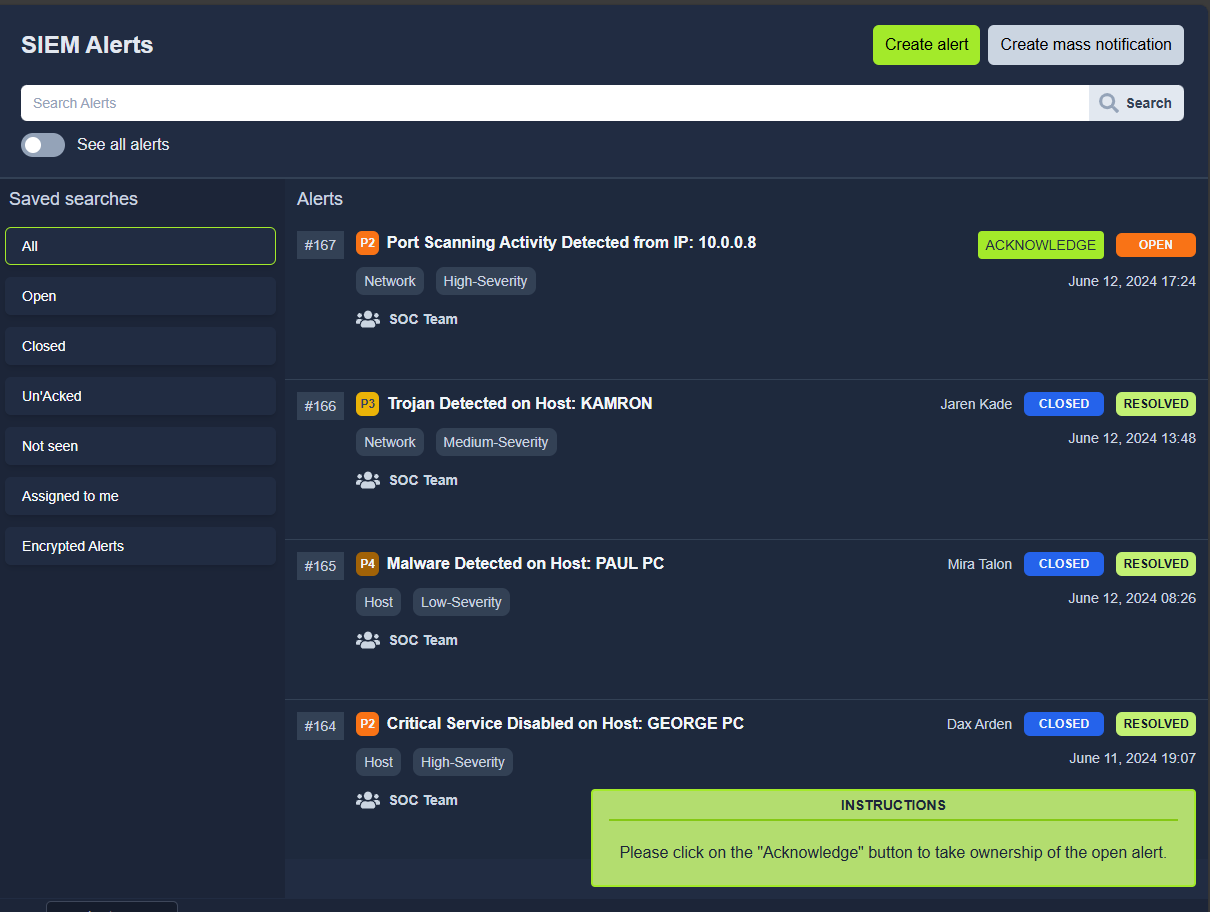
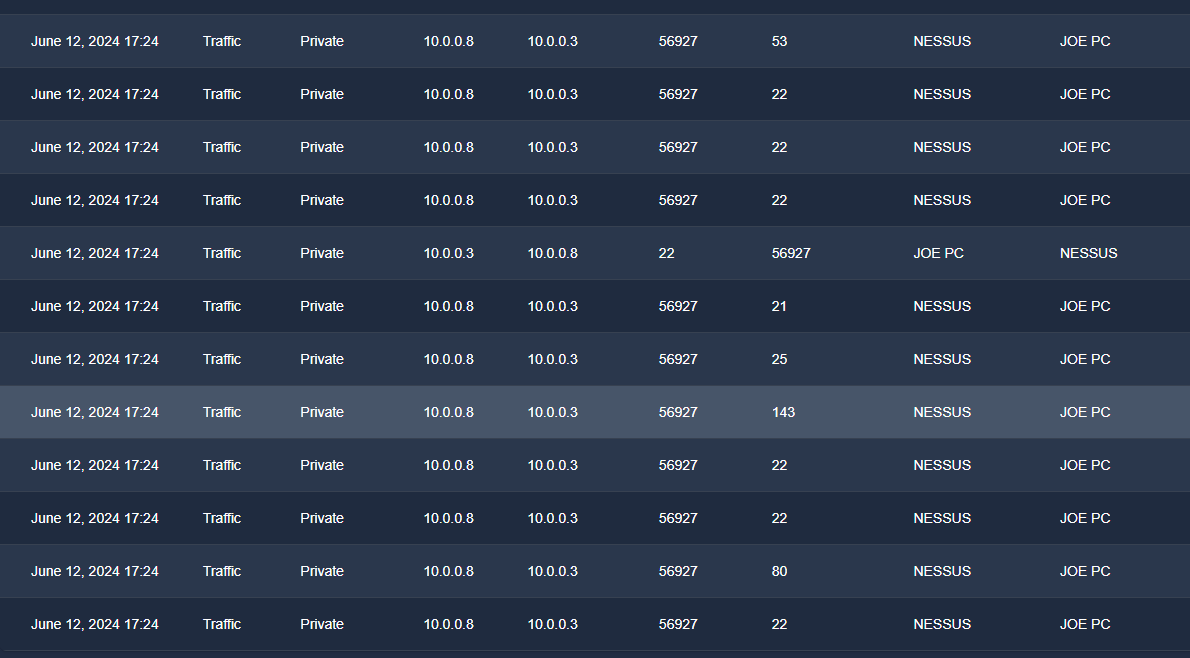
You are the Level 1 Analyst of your organization’s SOC team. You receive an alert that a port scanning activity has been observed on one of the hosts in the network. You have access to the SIEM solution, where you can see all the associated logs for this alert. You are tasked to view the logs individually and answer the question to the 5 Ws given below.
Note: The vulnerability assessment team notified the SOC team that they were running a port scan activity inside the network from the host: 10.0.0.8
What: Activity that triggered the alert?
Port Scan
When: Time of the activity?
June 12, 2024 17:24
Where: Destination host IP?
10.0.0.3
Who: Source host name?
NESSUS
Why: Reason for the activity? Intended/Malicious
Intended
Additional Investigation Notes: Has any response been sent back to the port scanner IP? (yea/nay)
Yea